“There are no differences but differences of degree between different degrees of
difference and no difference.”
― William James
__________________
Life begins and ends at the cellular level.
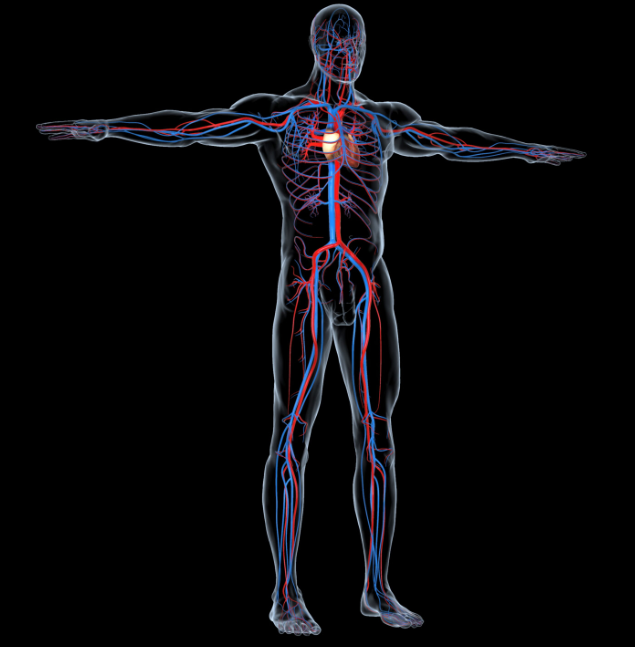
The complex human system includes a 60,000-mile vascular highway.
Nitric Oxide [NO] boasts its center-stage position because of its vital molecular presence in our bodies.
NO is endogenously generated from the amino acid L-arginine and molecular oxygen in reactions catalyzed by complex nitric oxide synthases.
It is a synergistic process fueled by protein-rich foods such as fish, red meat, poultry, soy, whole grains, beans, and dairy products. L-arginine can be used orally and topically as a supplement with the former being more effective.
Nitric oxide is important for your health for many reasons:
→ Promotes healthy circulation;
→ Optimizes oxygen and energy transport throughout the body;
→ Enhances blood vessel function;
→ Promotes healthy heart function;
→ Triggers signaling for healthy muscle contractions;
→ Augments endothelial health and proliferation;
→ Regulates blood pressure;
→ Mitigates insulin spikes

Why You Need Nitric Oxide
Your body uses nitric oxide to help regulate several functions – even though it is technically a free radical. Your body needs to make nitric oxide out of parts, which include vitamin C and nitrates. A shortfall means you will not be able to produce enough nitric oxide – this impacts several body systems:
Immune system: Your immune system is a large system full of many different varieties of cells. Nitric oxide helps these cells communicate and react more quickly to invaders.
Circulatory system: Nitric oxide appears to help your body dilate and constrict your blood vessels. This can improve your blood pressure and therefore your heart health.
Exercise and muscle performance: Nitric oxide may be correlated to a slight improvement in physical performance. Athletes who received nitrate supplements appear to tire slightly more slowly than those who do not receive the supplement.
Adding more nitrates to your diet may help boost nitric oxide levels and improve your exercise performance. This does mean you have the green light to consume more bacon and related processed foods.
There is a vast difference between nitrates in beets, for example, and processed-meat products. Nitrates from the latter often combine with the amino acids to form nitrosamines – which have been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers.
The nitrate–nitrite–NO pathway is a series of oxygen-independent and NO synthase–independent single-electron transfer reactions that ultimately facilitate vasodilation.
→ Regulate blood flow;
→ Cellular metabolism;
→ Cellular signaling;
→ Tissue protection during hypoxia and acidosis
There are two sources of nitrate and nitrite: the endogenous L-arginine/NO-synthase pathway [endothelial | eNOS] and the diet.
Endothelial NO is a significant signaling molecule that regulates cerebral blood flow playing a pivotal role in the prevention and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases.
The nitrate-nitrite-NO pathway has the potential to modify key physiologic abnormalities such as late systolic LV load from arterial wave reflections, arterial vasodilator reserve, muscle O2 delivery and utilization, and mitochondrial function which may lead to both immediate improvements in exercise tolerance and disease modifications.
NO is an essential component of the human body, involved in blood vessel dilation, stimulation of hormone release, signaling, and regulation of neurotransmission. Nitric oxide is synthesized by NO-synthase-dependent and –independent pathways.
The benefits to health span and lifespan cannot be understated. NO and healthy endothelium play critical roles in the following processes:
→ Vasodilation;
→ Platelet aggregation;
→ Monocyte adhesion;
→ Blood pressure regulation;
→ Superoxide radical elaboration;
→ LDL oxidation;
→ Muscle cell proliferation;
NO has two crucial functions. It keeps the arterial lining smooth and slippery, preventing white blood cells and platelets from latching on and causing damaging inflammation and artery-blocking blood clots.
NO has become a milestone in athlete physiology and pharmacology studies. The most known and remarkable function of NO is its role in controlling vasodilatation, blood rate, and mitochondrial respiration, thus enhancing performance.
Exercise and NO have a symbiotic relationship in that physical activity enhances NO production.
NO improves sports performance, promotes recovery, and benefits the athlete’s health with its physiological support in vasodilatation, blood flow, and mitochondrial respiration.

How to Boost NO
Several simple options exist to boost your NO levels. Replenishing NO levels is a 24/7 commitment since NO appears and disappears in the blink of an eye. Implementing some of the following strategies will help ensure your health is not compromised:
→ Exercise to enhance blood flow;
→ Consume vegetables high in nitrates;
→ Leafy greens – esp. spinach
→ Beets;
→ Celery:
→ Meat, poultry, and seafood;
→ Dark chocolate;
→ Garlic;
→ Citrus fruits;
→ Pomegranates;
→ Asparagus;
→ Brussels sprouts;
→ Cabbage;
→ Avocados;
→ Eggplant;
→ Increase antioxidant intake
→ Vitamin C;
→ Vitamin C;
→ Vitamin E;
→ Polyphenols;
→ Glutathione
→ Polyphenols;
→ Glutathione
→ Limit the use of mouthwash;
→ Nasal breathing;
→ Nadishodhana [alternate nostril breathing]
The foregoing approaches will ensure you are on the proper trail to health, performance, and longevity in the following areas:
→ Enhancing metabolism;
→ Increasing vasodilation;
→ Regulating hypertension;
→ Mitigating Periphery Artery Disease [PAD];
→ Decreasing angina risk;
→ Treating erectile dysfunction

Supplementation is an option if you determine it is impossible to enhance your NO levels and endothelium health via dietary and behavior modifications.
NO supplementation improves cardiac health, enhances performance during exercise, reduces high blood pressure during pregnancy, reduces erectile dysfunction, and improves healing processes and respiratory response.
L-arginine and L-citrulline supplementation contributes to nitric oxide levels because L-arginine is directly involved in NO synthesis, whereas L-citrulline acts as an L-arginine precursor that is further converted to NO by a reaction catalyzed by NO synthase.
The beauty of L-arginine is its benefits to several important areas in the complex human system:
→ Aging process;
→ Cardiovascular system;
→ Immune system;
→ Digestive system;
→ Metabolism;
→ Nervous system;
→ Muscoskeltal system;
→ Excretory system;
→ Sexual system;
→ Integumentary system
There are a plethora of NO supplement options on the market with various ingredients and side effects. One of the most researched is Neo40. Obtain the green light from your health practitioner before ingesting any NO supplements.
Backed by several clinical trials this proprietary, clinical strength, and patented Neo40 Professional formula is developed out of years of scientific research from the University of Texas Health Science Center and the NO Discovery Program.
This clinical-strength formula is biphasic – which allows for the conversion of nitrate to nitrite and then to NO in the endothelium as needed.
It is the most efficacious, concentrated, and convenient daily supplement to help quickly increase the body’s NO levels. Neo40 Professional offers significantly more NO production with each tablet than the flagship Neo40 Daily – with added methylfolate.
This is critical for those patients who have a methyl tetrahydrofolate reductase genetic variant [referred to as the MTHFR SNP] and SNPs in the NO Synthase [NOS] gene.
People with the MTHFR SNP cannot maintain enough reduced tetrahydrobiopterin to support endogenous NO production. The addition of L-methylfolate can help overcome this genetic issue.
Neo40 Professional may help promote:
→ Artery dilation for healthy blood flow;
→ Healthy blood pressure levels;
→ Cardiovascular and heart health;
→ Increased circulation throughout the body;
→ Healthy arterial function;
→ Healthy endothelium function
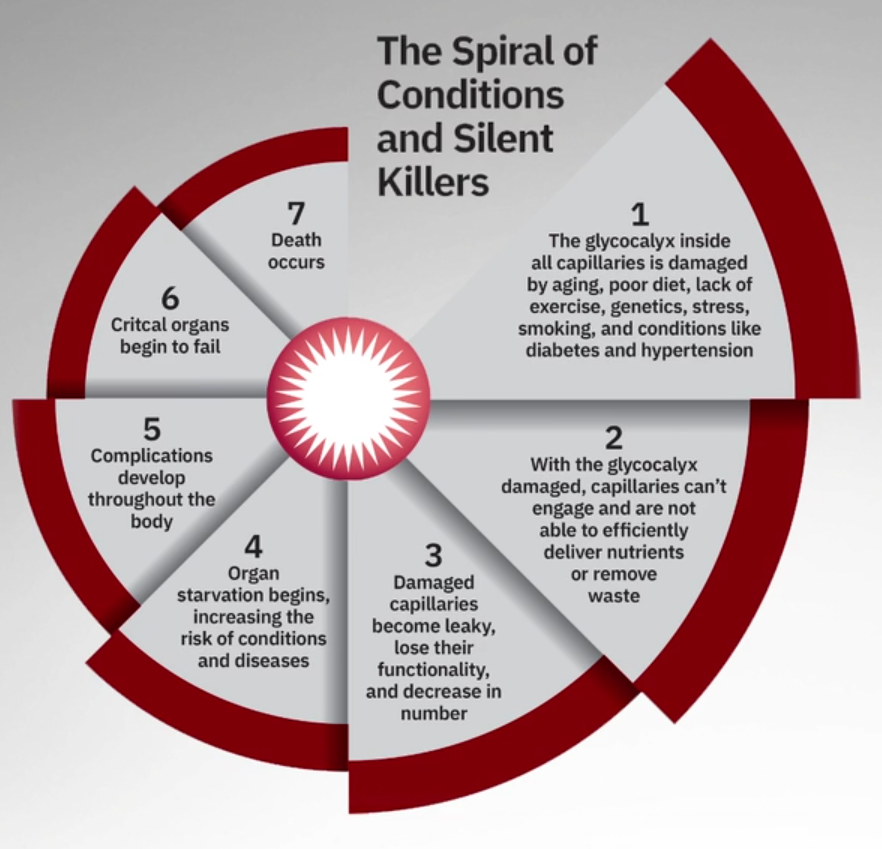
Enter Glycocalyx [aka EGX – Endothelial Glycocalyx]
Your microvascular system consists of arteries, capillaries, veins, and venules. NO is crucial for maintaining the health of the inner lining of blood vessels [endothelium].
Glycocalyx [Glyco Kay Licks | EGX] represents the thin, gel-like lining [endothelial membrane] that protects your vascular system. Its integrity is essential to the healthy function of all cells, organs, and bodily functions.
Each cell in your body is nourished by the blood that flows through the capillaries. Vital nutrients and oxygen are delivered while waste is removed from each cell. The proficiency of this remarkable process is eroded thanks to aging, genetics, and lifestyle choices.
Arteries transport oxygenated blood to tissue throughout your body. Veins carry venous [deoxygenated] blood toward the heart. After blood passes through the capillaries, it enters the smallest veins, called venules. From the venules, it flows into progressively larger veins until it reaches the heart.
EGX health is vital in enhancing the following:
→ Heart health;
→ Kidney health;
→ Brain health;
→ Sexual health
Science has shown that a compromised glycocalyx damages the microvascular system and leads to organ, muscle, and tissue starvation that insidiously leads to chronic and degenerative diseases pervasive in our society.
The importance of maintaining the glycocalyx cannot be overstated. An optimized glycocalyx promotes healthy organs associated with vascular health, ignites the bioavailability of nitric oxide, and supports nutrient and hormone exchange.
GlycoCheck is the only digital video microscope and software system that analyzes glycocalyx, endothelium, and capillary function, and objectively reports a single overall Microvascular Health Score.™
Clients can be tested to quantify capillary density, capillary blood volume, blood flow, red cell velocity, and endothelial glycocalyx function via non-invasive technology.
GlycoCheck measures and analyzes microvascular health and objectively reports one’s systemic microvascular health score [MVHS].
Lower scores represent links to diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, kidney disease, stroke, cognitive decline, septic shock, inflammatory disorders, and cancer metastasis.
NO is a signaling molecule involved in several physiological and pathological processes. It is crucial to your health, performance, and longevity. Consider its plethora of inside-out benefits since lifestyle choices and aging diminish its production in your body.
A limitless life is a choice…
Find more information at Performance Medicine™.
Schedule a FREE CONSULTATION via the blue widget, our contact form, or 401.207.4215.